Difference between revisions of "Warp"
m (→Time) |
(Added basic information about ship warp speed attribute) |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{hatnote|This article details warp travel. For information about sub-warp speeds, see [[Acceleration]].}} | |
| + | {{merge|Warp time calculation|Warp}} | ||
| + | '''Warp''' is the primary method of faster-than-light travel utilized by ships in New Eden. Warp travel is limited to transit between locations within the same solar system, and can only be initiated to locations at least 150 km away. The warp exit point is determined when the warp command is given. This is important if you warp to moving objects like fleet members. You also don't exit warp at the exact point but on a 3 km sphere around the point. This means you sometimes land outside of docking range of a station if you warp to it. This is the reason for [[instadock]] bookmarks. | ||
| − | + | == Warp Speed == | |
| − | Warp consists of | + | Ships have a Ship Warp Speed attribute. Different classes of ships have different base speeds, with [[Covert Ops]] and [[Interceptor]] frigates are the fastest at 8.00 AU/s while [[Freighters]] and [[Titans]] are the slowest at 1.37 AU/s. Here is a [[Travel_fits#Increasing_warp_speed|guide on increasing warp speed]]. |
| + | |||
| + | == Stages of warp == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Warp travel consists of three stages: | ||
# Acceleration | # Acceleration | ||
# Cruising | # Cruising | ||
# Deceleration | # Deceleration | ||
| − | Calculating the time taken to warp is done by calculating the time spent in each of these phases and adding them together. This requires calculating acceleration and deceleration time first, followed by cruise time. | + | It is possible to work out how long it should take for a ship to complete '''warp''' (once it enters warp) based on formulae released by CCP<ref>https://community.eveonline.com/news/dev-blogs/warp-drive-active</ref>. Calculating the time taken to warp is done by calculating the time spent in each of these phases and adding them together. This requires calculating acceleration and deceleration time first, followed by cruise time. This calculation does not include the time spent entering warp (accelerating to 75% of maximum velocity), or the time spent slowing after regaining control of the ship. |
| + | |||
| + | Total time in warp is given by: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>t_{total} = t_{accel} + t_{decel} + t_{cruise}</math> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Long warps== |
| + | A "long warp" is any warp where there is time to reach maximum warp speed before having to start decelerating. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Acceleration=== |
| − | |||
| − | <math> | + | ====The formulae==== |
| + | CCP provided formulae for both distance traveled and velocity reached after ''t'' seconds of acceleration. ''d'' is the distance in meters, ''v'' is speed in meters per second, ''k'' is the ship's warp speed (in AU/s) and ''a'' is 149,597,870,700 meters (1 AU). | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> | ||
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
d & = e^{kt} \\ | d & = e^{kt} \\ | ||
v & = k*e^{kt}\\ | v & = k*e^{kt}\\ | ||
| − | v_{ | + | v_{warp} & = k * a\\ |
\end{align} | \end{align} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <math> | + | ;Distance |
| + | To calculate distance traveled while accelerating: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> | ||
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
d & = e^{kt} \\ | d & = e^{kt} \\ | ||
| Line 35: | Line 49: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | The distance covered while accelerating to v<sub>warp</sub> is | + | The distance covered while accelerating to ''v<sub>warp</sub>'' is: |
| − | <math> | + | :<math> |
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
d_{accel} & = \frac{v_{warp}}{k} | d_{accel} & = \frac{v_{warp}}{k} | ||
| Line 47: | Line 61: | ||
This means that every ship covers exactly 1 AU while accelerating to its maximum warp speed. | This means that every ship covers exactly 1 AU while accelerating to its maximum warp speed. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ;Time | ||
To calculate the time spent accelerating to warp speed, the equation for ''v'' should be rearranged to be in terms of ''t'', and then solved for the case of ''v'' being equal to the warp speed (in m/s) | To calculate the time spent accelerating to warp speed, the equation for ''v'' should be rearranged to be in terms of ''t'', and then solved for the case of ''v'' being equal to the warp speed (in m/s) | ||
| − | <math> | + | :<math> |
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
v & = k*e^{kt}\\ | v & = k*e^{kt}\\ | ||
| Line 61: | Line 76: | ||
We want to find the time taken to maximum warp: | We want to find the time taken to maximum warp: | ||
| − | <math> | + | :<math> |
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
v_{warp} & = k * a\\ | v_{warp} & = k * a\\ | ||
t_{accel} & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{warp}}{k})}}{k}\\ | t_{accel} & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{warp}}{k})}}{k}\\ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
\end{align} | \end{align} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | ==Deceleration== | + | This formula can be simplified further to <math>\frac{\ln{a}}{k}</math>, although you may choose not to do this for implementation reasons. |
| − | Deceleration is calculated slightly differently. Instead of using ''k'' to calculate distance and velocity, it uses ''j'', which is defined as <math> | + | |
| + | ===Deceleration=== | ||
| + | Deceleration is calculated slightly differently. Instead of using ''k'' to calculate distance and velocity, it uses ''j'', which is defined as <math>\min(\frac{k}{3},2)</math>. A different rate of deceleration is used to prevent ships suddenly transitioning from "many, many AU away" to "on grid and out of warp" more rapidly than other pilots (or the server / client) can keep up with. | ||
There is a complication with deceleration calculations. Ships do not drop out of warp at 0 m/s. Instead, they drop out of warp at ''s'' m/s, after which normal sub-warp calculations take over. | There is a complication with deceleration calculations. Ships do not drop out of warp at 0 m/s. Instead, they drop out of warp at ''s'' m/s, after which normal sub-warp calculations take over. | ||
| − | <math> | + | :<math>s = \min(100, v_{subwarp}/2)</math> |
Where v<sub>subwarp</sub> is the maximum subwarp velocity of the ship; this varies greatly depending on the ship hull and pilot skills. | Where v<sub>subwarp</sub> is the maximum subwarp velocity of the ship; this varies greatly depending on the ship hull and pilot skills. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ;Distance | ||
This changes the formulae used slightly. Remember that distance travelled is the integral of velocity. | This changes the formulae used slightly. Remember that distance travelled is the integral of velocity. | ||
| − | <math> | + | :<math> |
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
v & = k * e^{jt}\\ | v & = k * e^{jt}\\ | ||
| − | + | d & = \int_{0}^{t}k*e^{j⋅dx}\,dx = \frac{k*e^{jt}}{j}\\ | |
& = \frac{v}{j} | & = \frac{v}{j} | ||
\end{align} | \end{align} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | The distance covered while decelerating from v<sub>warp</sub> is | + | The distance covered while decelerating from ''v<sub>warp</sub>'' is |
| − | <math> | + | :<math> |
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
d_{decel} & = \frac{v_{warp}}{j} | d_{decel} & = \frac{v_{warp}}{j} | ||
| Line 99: | Line 115: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | Note that for ships that travel at up to 6 AU/s, k / j = k / (k/3) = 3, so these ships cover 3 AU while decelerating. The complication of not stopping warp at 0 can be safely ignored for distance calculations, because the distance that would be covered while decelerating from 100 m/s is insignificant compared to the ~450 billion meters it takes to decelerate from warp speed to warp drop speed. | + | Note that for ships that travel at up to 6 AU/s, ''k'' / ''j'' = ''k'' / (''k''/3) = 3, so these ships cover 3 AU while decelerating. The complication of not stopping warp at 0 can be safely ignored for distance calculations, because the distance that would be covered while decelerating from 100 m/s is insignificant compared to the ~450 billion meters it takes to decelerate from warp speed to warp drop speed. |
| − | + | ||
| + | ;Time | ||
As with acceleration, time to decelerate from maximum warp velocity is worked out by rearranging the velocity equation. | As with acceleration, time to decelerate from maximum warp velocity is worked out by rearranging the velocity equation. | ||
| − | <math> | + | :<math> |
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
v &= k*e^{jt}\\ | v &= k*e^{jt}\\ | ||
| Line 114: | Line 131: | ||
While the deceleration from ''s'' to 0 was insignificant in terms of distance, it is significant in terms of time. This means that the time to decelerate is calculated as follows: | While the deceleration from ''s'' to 0 was insignificant in terms of distance, it is significant in terms of time. This means that the time to decelerate is calculated as follows: | ||
| − | <math> | + | :<math> |
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
t_{decel} & = t_{decel\_warp} - t_{decel\_s}\\ | t_{decel} & = t_{decel\_warp} - t_{decel\_s}\\ | ||
| − | & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{ | + | & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{warp}}{k})}}{j} - \frac{\ln{(\frac{s}{k})}}{j}\\ |
| − | & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{ | + | & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{warp}}{k})} - \ln{(\frac{s}{k})}}{j}\\ |
| − | & = \frac{\ln{ | + | & = \frac{\ln{v_{warp}} - \ln{k} - \ln{s} + \ln{k}}{j}\\ |
| − | & = \frac{\ln{ | + | & = \frac{\ln{v_{warp}} - \ln{s}}{j}\\ |
| − | & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{ | + | & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{warp}}{s})}}{j} |
\end{align} | \end{align} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | ==Cruising== | + | ===Cruising=== |
| − | + | ;Distance | |
The distance covered while cruising is the total warp distance minus any distance covered while accelerating or decelerating. | The distance covered while cruising is the total warp distance minus any distance covered while accelerating or decelerating. | ||
| − | <math> | + | :<math>d_{cruise} = d_{total} - d_{accel} - d_{decel}</math> |
For all but the fastest ships, this will be ''d<sub>total</sub> - 4 AU''. | For all but the fastest ships, this will be ''d<sub>total</sub> - 4 AU''. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <math>\ | + | ;Time |
| + | Time spent cruising is: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>t_{cruise} = \frac{d_{cruise}}{v_{warp}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Short Warps== | ||
| + | The above calculations work as long as some time is spent at maximum warp speed; <math>d_{total} \geq d_{accel} + d_{decel}</math>. If the warp is short enough that the ship never reaches top speed, a different set of calculations are needed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | \begin{align} | ||
| + | d_{accel} & = \frac{v_{max}}{k}, d_{decel} = \frac{v_{max}}{j}\\ | ||
| + | d_{total} & = d_{accel} + d_{decel} = v_{max}(\frac{1}{k} + \frac{1}{j})\\ | ||
| + | v_{max} & = \frac{d_{total}*k*j}{k + j} | ||
| + | \end{align} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This enables the calculation of new acceleration and deceleration times using the formulae described in the previous sections, but substituting in the new ''v<sub>max</sub>'': | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | \begin{align} | ||
| + | t_{accel} & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{max}}{k})}}{k}\\ | ||
| + | t_{decel} & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{max}}{s})}}{j}\\ | ||
| + | t_{total} & = t_{accel} + t_{decel} | ||
| + | \end{align} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Implementation== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following python code is one possible implementation of the above. It attempts to generate the same data as presented by CCP in the forums. It matches with their numbers, except for 50 AU titan warps, which are one second out. Note that the sub warp speed of the ship is fixed at 200 m/s. This is because the CCP-produced tables assume that every ship drops out of warp at 100 m/s<ref>https://forums.eveonline.com/default.aspx?g=posts&m=3902148#post3902148</ref>. If trying to run calculations for actual ships, this value will need to be replaced with a more appropriate one. The output values are also passed through the ceil() function, as this is what seems to match the rounding mode that CCP used.<ref>http://content.eveonline.com/www/newssystem/media/65418/1/numbers_table.png</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | import math | ||
| + | AU_IN_M=149597870700 | ||
| + | |||
| + | def get_distance(dist): | ||
| + | if dist > 1e9: | ||
| + | return (dist / AU_IN_M, "AU") | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | return (dist/1000, "KM") | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Warp speed in AU/s, subwarp speed in m/s, distance in m | ||
| + | def calculate_time_in_warp(max_warp_speed, max_subwarp_speed, warp_dist): | ||
| + | |||
| + | k_accel = max_warp_speed | ||
| + | k_decel = min(max_warp_speed / 3, 2) | ||
| + | |||
| + | warp_dropout_speed = min(max_subwarp_speed / 2, 100) | ||
| + | max_ms_warp_speed = max_warp_speed * AU_IN_M | ||
| + | |||
| + | accel_dist = max_ms_warp_speed / k_accel | ||
| + | decel_dist = max_ms_warp_speed / k_decel | ||
| + | |||
| + | minimum_dist = accel_dist + decel_dist | ||
| + | |||
| + | cruise_time = 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | if minimum_dist > warp_dist: | ||
| + | max_ms_warp_speed = warp_dist * k_accel * k_decel / (k_accel + k_decel) | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | cruise_time = (warp_dist - minimum_dist) / max_ms_warp_speed | ||
| + | |||
| + | accel_time = math.log(max_ms_warp_speed / k_accel) / k_accel | ||
| + | decel_time = math.log(max_ms_warp_speed / warp_dropout_speed) / k_decel | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | total_time = cruise_time + accel_time + decel_time | ||
| + | distance = get_distance(warp_dist) | ||
| + | return total_time | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | distances = [150e3, 1e9, AU_IN_M * 1, AU_IN_M * 2, AU_IN_M * 5, AU_IN_M * 10, AU_IN_M * 20, AU_IN_M * 50, AU_IN_M * 100, AU_IN_M * 200] | ||
| + | speeds = [1.36, 1.5, 2, 2.2, 2.5, 2.75, 3, 3.3, 4.5, 5, 5.5, 6, 8] | ||
| + | |||
| + | result = {} | ||
| + | for speed in speeds: | ||
| + | for dist in distances: | ||
| + | result[(dist, speed)] = calculate_time_in_warp(speed, 200, dist) | ||
| + | |||
| + | print("{:9s}".format(""), end="") | ||
| + | for speed in speeds: | ||
| + | print("{:9.2f}".format(speed), end="") | ||
| + | |||
| + | last_dist = 1e999 | ||
| + | for x,y in sorted(result.keys()): | ||
| + | dist = get_distance(x) | ||
| + | if (y < last_dist): | ||
| + | print("\n{:7.5n} {:s}".format(dist[0],dist[1]), end="") | ||
| + | last_dist = y | ||
| + | |||
| + | print("{:9.0f}".format(math.ceil(result[x,y])), end="") | ||
| + | |||
| + | print() | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Output=== | ||
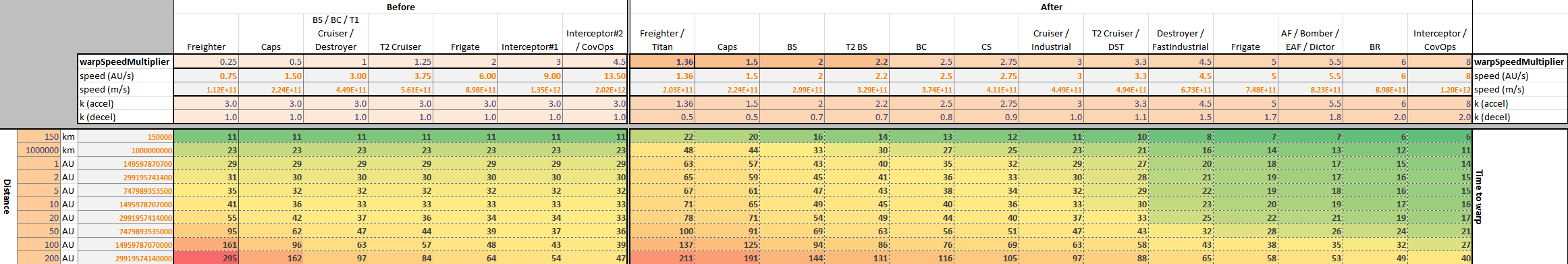
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Warp Speed (AU/s) | ||
| + | Distance 1.36 1.50 2.00 2.20 2.50 2.75 3.00 3.30 4.50 5.00 5.50 6.00 8.00 | ||
| + | 150 KM 22 20 16 14 13 12 11 10 8 7 7 6 6 | ||
| + | 1e+06 KM 48 44 33 30 27 25 23 21 16 14 13 12 11 | ||
| + | 1 AU 63 57 43 40 35 32 29 27 20 18 17 15 14 | ||
| + | 2 AU 65 59 45 41 36 33 30 28 21 19 17 16 15 | ||
| + | 5 AU 67 61 47 43 38 34 32 29 22 19 18 16 15 | ||
| + | 10 AU 71 65 49 45 40 36 33 30 23 20 19 17 16 | ||
| + | 20 AU 78 71 54 49 44 40 37 33 25 22 21 19 17 | ||
| + | 50 AU 100 91 69 63 56 51 47 43 32 28 26 24 21 | ||
| + | 100 AU 137 125 94 86 76 69 63 58 43 38 35 32 27 | ||
| + | 200 AU 211 191 144 131 116 105 97 88 65 58 53 49 40 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =References= | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
| + | =See also= | ||
| + | *[https://support.eveonline.com/hc/en-us/articles/115004925685-System-Travel-Warping Helpdesk Warping] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Game mechanics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:30, 7 June 2024
- This article details warp travel. For information about sub-warp speeds, see Acceleration.
Warp is the primary method of faster-than-light travel utilized by ships in New Eden. Warp travel is limited to transit between locations within the same solar system, and can only be initiated to locations at least 150 km away. The warp exit point is determined when the warp command is given. This is important if you warp to moving objects like fleet members. You also don't exit warp at the exact point but on a 3 km sphere around the point. This means you sometimes land outside of docking range of a station if you warp to it. This is the reason for instadock bookmarks.
Warp Speed
Ships have a Ship Warp Speed attribute. Different classes of ships have different base speeds, with Covert Ops and Interceptor frigates are the fastest at 8.00 AU/s while Freighters and Titans are the slowest at 1.37 AU/s. Here is a guide on increasing warp speed.
Stages of warp
Warp travel consists of three stages:
- Acceleration
- Cruising
- Deceleration
It is possible to work out how long it should take for a ship to complete warp (once it enters warp) based on formulae released by CCP[1]. Calculating the time taken to warp is done by calculating the time spent in each of these phases and adding them together. This requires calculating acceleration and deceleration time first, followed by cruise time. This calculation does not include the time spent entering warp (accelerating to 75% of maximum velocity), or the time spent slowing after regaining control of the ship.
Total time in warp is given by:
- [math]t_{total} = t_{accel} + t_{decel} + t_{cruise}[/math]
Long warps
A "long warp" is any warp where there is time to reach maximum warp speed before having to start decelerating.
Acceleration
The formulae
CCP provided formulae for both distance traveled and velocity reached after t seconds of acceleration. d is the distance in meters, v is speed in meters per second, k is the ship's warp speed (in AU/s) and a is 149,597,870,700 meters (1 AU).
- [math] \begin{align} d & = e^{kt} \\ v & = k*e^{kt}\\ v_{warp} & = k * a\\ \end{align} [/math]
- Distance
To calculate distance traveled while accelerating:
- [math] \begin{align} d & = e^{kt} \\ v & = k*e^{kt}\\ & = k*d\\ \therefore d & = \frac{v}{k} \end{align} [/math]
The distance covered while accelerating to vwarp is:
- [math] \begin{align} d_{accel} & = \frac{v_{warp}}{k} & = \frac{k*a}{k} & = a \end{align} [/math]
This means that every ship covers exactly 1 AU while accelerating to its maximum warp speed.
- Time
To calculate the time spent accelerating to warp speed, the equation for v should be rearranged to be in terms of t, and then solved for the case of v being equal to the warp speed (in m/s)
- [math] \begin{align} v & = k*e^{kt}\\ \frac{v}{k} & = e^{kt}\\ kt & = \ln{(\frac{v}{k})}\\ t & =\frac{\ln{(\frac{v}{k})}}{k}\\ \end{align} [/math]
We want to find the time taken to maximum warp:
- [math] \begin{align} v_{warp} & = k * a\\ t_{accel} & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{warp}}{k})}}{k}\\ \end{align} [/math]
This formula can be simplified further to [math]\frac{\ln{a}}{k}[/math], although you may choose not to do this for implementation reasons.
Deceleration
Deceleration is calculated slightly differently. Instead of using k to calculate distance and velocity, it uses j, which is defined as [math]\min(\frac{k}{3},2)[/math]. A different rate of deceleration is used to prevent ships suddenly transitioning from "many, many AU away" to "on grid and out of warp" more rapidly than other pilots (or the server / client) can keep up with.
There is a complication with deceleration calculations. Ships do not drop out of warp at 0 m/s. Instead, they drop out of warp at s m/s, after which normal sub-warp calculations take over.
- [math]s = \min(100, v_{subwarp}/2)[/math]
Where vsubwarp is the maximum subwarp velocity of the ship; this varies greatly depending on the ship hull and pilot skills.
- Distance
This changes the formulae used slightly. Remember that distance travelled is the integral of velocity.
- [math] \begin{align} v & = k * e^{jt}\\ d & = \int_{0}^{t}k*e^{j⋅dx}\,dx = \frac{k*e^{jt}}{j}\\ & = \frac{v}{j} \end{align} [/math]
The distance covered while decelerating from vwarp is
- [math] \begin{align} d_{decel} & = \frac{v_{warp}}{j} = \frac{k*a}{j} \end{align} [/math]
Note that for ships that travel at up to 6 AU/s, k / j = k / (k/3) = 3, so these ships cover 3 AU while decelerating. The complication of not stopping warp at 0 can be safely ignored for distance calculations, because the distance that would be covered while decelerating from 100 m/s is insignificant compared to the ~450 billion meters it takes to decelerate from warp speed to warp drop speed.
- Time
As with acceleration, time to decelerate from maximum warp velocity is worked out by rearranging the velocity equation.
- [math] \begin{align} v &= k*e^{jt}\\ \frac{v}{k} & = e ^ {jt}\\ t & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v}{k})}}{j} \end{align} [/math]
While the deceleration from s to 0 was insignificant in terms of distance, it is significant in terms of time. This means that the time to decelerate is calculated as follows:
- [math] \begin{align} t_{decel} & = t_{decel\_warp} - t_{decel\_s}\\ & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{warp}}{k})}}{j} - \frac{\ln{(\frac{s}{k})}}{j}\\ & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{warp}}{k})} - \ln{(\frac{s}{k})}}{j}\\ & = \frac{\ln{v_{warp}} - \ln{k} - \ln{s} + \ln{k}}{j}\\ & = \frac{\ln{v_{warp}} - \ln{s}}{j}\\ & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{warp}}{s})}}{j} \end{align} [/math]
Cruising
- Distance
The distance covered while cruising is the total warp distance minus any distance covered while accelerating or decelerating.
- [math]d_{cruise} = d_{total} - d_{accel} - d_{decel}[/math]
For all but the fastest ships, this will be dtotal - 4 AU.
- Time
Time spent cruising is:
- [math]t_{cruise} = \frac{d_{cruise}}{v_{warp}}[/math]
Short Warps
The above calculations work as long as some time is spent at maximum warp speed; [math]d_{total} \geq d_{accel} + d_{decel}[/math]. If the warp is short enough that the ship never reaches top speed, a different set of calculations are needed.
- [math] \begin{align} d_{accel} & = \frac{v_{max}}{k}, d_{decel} = \frac{v_{max}}{j}\\ d_{total} & = d_{accel} + d_{decel} = v_{max}(\frac{1}{k} + \frac{1}{j})\\ v_{max} & = \frac{d_{total}*k*j}{k + j} \end{align} [/math]
This enables the calculation of new acceleration and deceleration times using the formulae described in the previous sections, but substituting in the new vmax:
- [math] \begin{align} t_{accel} & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{max}}{k})}}{k}\\ t_{decel} & = \frac{\ln{(\frac{v_{max}}{s})}}{j}\\ t_{total} & = t_{accel} + t_{decel} \end{align} [/math]
Implementation
The following python code is one possible implementation of the above. It attempts to generate the same data as presented by CCP in the forums. It matches with their numbers, except for 50 AU titan warps, which are one second out. Note that the sub warp speed of the ship is fixed at 200 m/s. This is because the CCP-produced tables assume that every ship drops out of warp at 100 m/s[2]. If trying to run calculations for actual ships, this value will need to be replaced with a more appropriate one. The output values are also passed through the ceil() function, as this is what seems to match the rounding mode that CCP used.[3]
import math
AU_IN_M=149597870700
def get_distance(dist):
if dist > 1e9:
return (dist / AU_IN_M, "AU")
else:
return (dist/1000, "KM")
# Warp speed in AU/s, subwarp speed in m/s, distance in m
def calculate_time_in_warp(max_warp_speed, max_subwarp_speed, warp_dist):
k_accel = max_warp_speed
k_decel = min(max_warp_speed / 3, 2)
warp_dropout_speed = min(max_subwarp_speed / 2, 100)
max_ms_warp_speed = max_warp_speed * AU_IN_M
accel_dist = max_ms_warp_speed / k_accel
decel_dist = max_ms_warp_speed / k_decel
minimum_dist = accel_dist + decel_dist
cruise_time = 0
if minimum_dist > warp_dist:
max_ms_warp_speed = warp_dist * k_accel * k_decel / (k_accel + k_decel)
else:
cruise_time = (warp_dist - minimum_dist) / max_ms_warp_speed
accel_time = math.log(max_ms_warp_speed / k_accel) / k_accel
decel_time = math.log(max_ms_warp_speed / warp_dropout_speed) / k_decel
total_time = cruise_time + accel_time + decel_time
distance = get_distance(warp_dist)
return total_time
distances = [150e3, 1e9, AU_IN_M * 1, AU_IN_M * 2, AU_IN_M * 5, AU_IN_M * 10, AU_IN_M * 20, AU_IN_M * 50, AU_IN_M * 100, AU_IN_M * 200]
speeds = [1.36, 1.5, 2, 2.2, 2.5, 2.75, 3, 3.3, 4.5, 5, 5.5, 6, 8]
result = {}
for speed in speeds:
for dist in distances:
result[(dist, speed)] = calculate_time_in_warp(speed, 200, dist)
print("{:9s}".format(""), end="")
for speed in speeds:
print("{:9.2f}".format(speed), end="")
last_dist = 1e999
for x,y in sorted(result.keys()):
dist = get_distance(x)
if (y < last_dist):
print("\n{:7.5n} {:s}".format(dist[0],dist[1]), end="")
last_dist = y
print("{:9.0f}".format(math.ceil(result[x,y])), end="")
print()
Output
Warp Speed (AU/s)
Distance 1.36 1.50 2.00 2.20 2.50 2.75 3.00 3.30 4.50 5.00 5.50 6.00 8.00
150 KM 22 20 16 14 13 12 11 10 8 7 7 6 6
1e+06 KM 48 44 33 30 27 25 23 21 16 14 13 12 11
1 AU 63 57 43 40 35 32 29 27 20 18 17 15 14
2 AU 65 59 45 41 36 33 30 28 21 19 17 16 15
5 AU 67 61 47 43 38 34 32 29 22 19 18 16 15
10 AU 71 65 49 45 40 36 33 30 23 20 19 17 16
20 AU 78 71 54 49 44 40 37 33 25 22 21 19 17
50 AU 100 91 69 63 56 51 47 43 32 28 26 24 21
100 AU 137 125 94 86 76 69 63 58 43 38 35 32 27
200 AU 211 191 144 131 116 105 97 88 65 58 53 49 40