More actions
| Line 248: | Line 248: | ||
When the target's signature radius is larger than the missile's explosion radius, <code>S/E</code> will be greater than 1, and that term will be rejected. If <code>S</code> is smaller than <code>E</code>, then <code>S/E</code> will be computed and compared with the third term. The smaller of these will be chosen and multiplied times the Base Damage. | When the target's signature radius is larger than the missile's explosion radius, <code>S/E</code> will be greater than 1, and that term will be rejected. If <code>S</code> is smaller than <code>E</code>, then <code>S/E</code> will be computed and compared with the third term. The smaller of these will be chosen and multiplied times the Base Damage. | ||
Since the part of the equation that is affected by velocity ... <code>(S/E*Ve/Vt)^ADRF</code> ... only matters if it is less than 1, it can be set to 1 and solved to find the point where it begins to matter. Doing that gives <code>Vt = | Since the part of the equation that is affected by velocity ... <code>(S/E*Ve/Vt)^ADRF</code> ... only matters if it is less than 1, it can be set to 1 and solved to find the point where it begins to matter. Doing that gives <code>Vt = S/ (1^(1/ ADRF) * E) * Ve</code>. Since <code>1^x = 1</code>, then <code>1^(1/ ADRF) </code> also must equal 1, and the equation reduces to <code>Vt = (S/E) * Ve</code>. This can be rewritten as | ||
Vt = S * Ve/E | Vt = S * Ve/E | ||
Revision as of 12:21, 10 November 2016
| Weapon Systems |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Other Weapon Systems |
| Other Mechanics |
- This document is concerned only with the damage that is created when a missile explodes near a ship. It specifically does not cover aspects of missile weaponry such as launcher speed or missile flight time. Nor does it concern itself with the ultimate damage to the ship, which may be shielded or armored against the kind of damage that the missile creates.
The Basic Picture
All ships are surrounded by an invisible bubble called its signature radius. This is the area that weapons see when they try to lock on to the ship. Generally, the bigger the ship, the bigger the bubble. (However, various things can extend or shrink the size of a ship's signature radius.)
When a missile crosses the signature radius of its target, it explodes. The explosion expands in a bubble of its own. The speed at which this bubble grows is called the explosion velocity, and the maximum size that the bubble will reach is called the explosion radius.
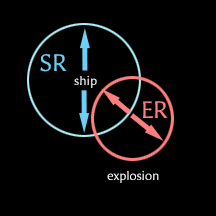
The missile does not so much hit the ship as explode near it. EVE uses a mathematical equation to compute the precise amount of damage that the explosion does to the ship. You can read about the details in the technical section of this document. The next section explains the way that missile damage is computed in general terms.
When a Missile Explodes
Every missile has a Base Damage – which is listed as "explosive damage", "kinetic damage", or so on in the Attributes tab of the missile's Get Info window.
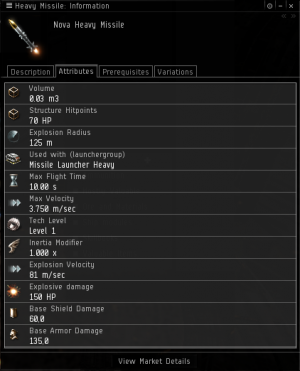
This amount may be augmented somewhat by certain skills and/or equipment, and when the term "Base Damage" is used here, it means the listed damage of the missile plus any augmented damage … in other words, the damage you expect the missile to do if it scores a direct hit.
While a missile can apply up to 100% of the Base Damage to a ship in some situations, damage is often reduced by two factors:
- If the target ship is moving faster than the explosion velocity of the missile. Think of this as a fast ship being able to somewhat outrun the explosion.
- If the signature radius of the target ship is smaller than explosion radius of the missile. Think of this as a small ship flying through a large explosion and only being hit by a part of it.
In practice damage is usually reduced by the combination of these two factors.
Explosion Details
If you have been using missiles, this probably does not surprise you, and you may want more details, but since the actual damage number depends on target speed, missile speed, signature radius and so on, there is no way to give a simple summary or table of how much damage a particular kind of missile will do against a particular kind of ship.
Without going into the mathematical details (which are discussed below), the other factors that might come into play are these:
- If you are using missiles, you want a faster explosion (more explosion velocity) and a smaller one (less explosion radius) – in other words, a short, tight explosion is more effective than a long, loose one.
- If a missile reaches its target, it will always do some damage. It is the speed of the explosion that helps determine how much ... not the speed of the missile.
- Unlike with turrets, the angular velocity of the target does not matter for computing damage. The missile still has to get to the target, but once it arrives, damage is computed using the target's absolute velocity.
- Because damage is related to both speed and Signature Ratio, using a microwarp drive, which increases both speed AND Signature Ratio, will not significantly reduce damage. Afterburners do not affect Signature Ratio, however, and so could possibly help.
An Illustration
As an illustration, here are the basic statistics for the Inferno Light Missile. These are sorted on explosion velocity.
| Missile | Explosion Radius | Explosion Velocity | Base Damage (Thermal) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inferno Precision Light Missile | 25 | 204 | 83 |
| Inferno Light Missile | 40 | 170 | 83 |
| Caldari Navy Inferno Light Missile | 40 | 170 | 95 |
| Inferno Fury Light Missile | 69 | 143 | 116 |
First, notice that the only difference between the regular Inferno and the Caldari Navy Inferno is a change in the base damage.
Second, you can see that the Fury missile has a larger base damage, but that the Precision missile has a faster Explosion Velocity and smaller Explosion Radius.
Explosion radius and velocity come into play whenever the target is small and/or fast. This means that the Fury missile will deliver its full damage against a bigger, slower ship, but is more likely to have its damage reduced against smaller, faster targets. A Precision missile will also deliver its full damage against a bigger, slower ship – though it will do less damage than the Fury because of the lower base damage – but it will also be more likely to deliver full damage to smaller, faster ships.
Other classes of missiles follow the same pattern. Again, the list is sorted on explosion velocity.
| Missile | Explosion Radius | Explosion Velocity | Base Damage (Thermal) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inferno Light Missile | 40 | 170 | 83 |
| Inferno Rocket | 20 | 150 | 33 |
| Inferno Heavy Missile | 140 | 81 | 135 |
| Inferno Torpedo | 450 | 71 | 450 |
Rockets have the smallest Base Damage (BD), but they have a very small explosion radius (ER) and a fairly fast explosion velocity (EV). So, you would expect them to do very good damage to small targets (due to their ER and EV), but relatively less damage to large ones (due to their BD). Torpedoes have five times the base damage of Light Missiles, but they have ten times the explosion radius and half the explosion velocity. So, you would expect Torpedoes to be very good against large, slow ships (due to their BD), but very poor against small, fast ships (due to their ER and EV).
If that all makes sense, then good ... if not, then just keep in mind that, all things being equal, EVE has balanced the damage done by missiles among themselves as well as with the damage done by projectiles, beams and other types of weapons.
How to Increase the Damage of Your Missiles
Skills and ship equipment can have a direct impact on missile damage. A number of implants do the same. In addition, modules such as Target Painters and Webifiers can affect the target's signature radius and speed, thus making missile damage more effective.
Skills
While various skills improve a player's expertise with missiles, these three specifically affect the amount of damage done when a missile explodes.
- Guided Missile Precision (5x) reduces the impact of the target signature radius on the damage. This effectively decreases the explosion radius of the missile by 5% per skill level, which makes it more likely to do full damage to a small/fast target.
- Target Navigation Prediction (2x) reduces the impact of the target velocity on the damage. This effectively increases the explosion velocity by 10% per skill level, which makes it more likely to do full damage to a small/fast target.
- Warhead Upgrades (5x) provides a 2% increase in missile damage per level ... this appears to apply to Base Damage.
Modules, Rigs and Ammunition
While there are additional items that affect missiles and launchers, those do not alter the missile damage as such. Here are the ones that do.
Ballistic Control System: among other things, gives a bonus to base missile damage.
- Warhead Calefaction Catalyst: increases the base damage of the missile but increases the CPU requirement for the launcher.
- Warhead Flare Catalyst: increases the explosion velocity of the missile but increases the CPU requirement for the launcher.
- Warhead Rigor Catalyst: decreases the explosion radius of the missile but increases the CPU requirement for the launcher.
- Precision Missiles are more effective than Furies against smaller, faster targets, but do less base damage per missile.
- Fury Missiles have a larger base damage per missile, but are less effective than Precisions against smaller, faster targets.
- Both have a somewhat shorter range than regular and Faction missiles.
Implants
A variety of Hardwired Implants affect weapons systems. Only a few have a direct impact on missile damage creation.
Specific Missile Classes
- Zainou 'Snapshot' Cruise Missiles: 1% to 6% bonus to the base damage of Cruise Missiles
- Zainou 'Snapshot' Torpedoes: 1% to 6% bonus to the base damage of Torpedos
- Zainou 'Snapshot' Heavy Missiles: 1% to 6% bonus to the base damage of Heavy Missiles
- Zainou 'Snapshot' Assault Missiles: 1% to 6% bonus to the base damage of Assault Missiles
- Zainou 'Snapshot' Rockets: 1% to 6% bonus to the base damage of Rockets
- Zainou 'Snapshot' FOF Explosion Radius: 1% to 6% bonus to explosion radius of Auto-Target Missiles
All Missiles
- Zainou 'Deadeye' Guided Missile Precision: 1% to 6% reduced factor of signature radius for all missile explosions
- Zainou 'Deadeye' Target Navigation Prediction: 1% to 6% decrease in factor of target's velocity for all missile explosions
Affecting the Target Ship
Missile damage can be substantially increased by using Electronic Warfare Modules to change the Velocity and/or Signature Radius of the target ship.
- Target Painters can effectively increase the Signature Radius of the ship. This makes the ship bigger and more likely to take full damage.
- Stasis Webifiers can decrease the ship's velocity. This makes the ship slower and more likely to take full damage.
Note that both of these are most effective if you are firing missiles at small, fast ships. They may be completely unhelpful if you are firing at very large ships.
Technical Section: The Missile Damage Equation
This section discusses the mathematical equation that governs how much damage missile explosions create.
Here is the equation for missile damage:
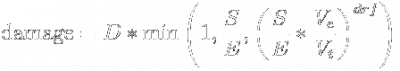
Here are the terms in the equation. Except for the "damage reduction factor", these are the same as were defined in the Basic Picture section, above :
| S | signature radius of target | Note: The bigger the better | |
| Vt | velocity of target | Note: The smaller the better | |
| D | base damage of missile | Note: The bigger the better | |
| E | explosion radius of missile | Note: The smaller the better | |
| Ve | explosion velocity of missile | Note: The bigger the better | |
| drf | damage reduction factor | Note: The smaller the better | Note: as of EVE release 118.6, the element [ln(drf)/ln(5.5)] has been replaced by a single pre-calculated value. This results in no change in game play. The new term is called "AOE Damage Reduction Factor". See EVE forum for more. |
Unlike the turret damage equation, missile damage takes the absolute velocity of the target into account, not the angular velocity. To create missile damage, the game computes two values. These values are compared to 1, and the smallest is chosen. That number is then multiplied by the base damage to get the amount of damage applied to the ship.
The Target Values
Target velocity (Vt) is the speed of the target. The maximum speed of a ship can be found in its description, but this speed will vary from the maximum during combat. Keep in mind that the speed of the missile is not a factor. What matters is the speed of the ship at the time the missile arrives.
Target signature radius (S) is the effective size of a ship. It is affected by various factors, such as the ship type, modules, rigs, skills and/or implants. It cannot displayed in the Overview, but it is listed in the ship's Get Info Attributes.
The Missile Values
The base damage of a missile (D) can be found in the missile information under “EM damage”, “Kinetic damage”, “Thermal damage” or “Explosive damage”. Base Shield Damage and Base Armor Damage are not relevant for this calculation.
The explosion radius of a missile (E) represents the size of the explosion. It can be found in the missile information under “Explosion radius”.
The explosion velocity of missile (Ve) is the rate of expansion of the explosion. It can be found in the missile information under “Explosion velocity”.
All three of these can be improved through the use of rigs and/or implants.
Finding the Damage Reduction Factor of a Missile
The “damage reduction factor” (drf) of a missile is not mentioned in the game, it is however included in the data that CCP publishes, and you can easily view it in the EVEMon item browser. You can also see the value 5.5 from the above equation in the same data – it is called the damage reduction sensitivity.
| Missile Type | DRF |
|---|---|
| Precision Light Missile | 2.6 |
| Precision Heavy Missile | 2.7 |
| Auto-Targeting Light Missile | 2.8 |
| Light Missile | 2.8 |
| Rocket | 3 |
| Heavy Missile | 3.2 |
| Auto-Targeting Heavy Missile | 3.2 |
| Javelin Rocket | 3.2 |
| Fury Light Missile | 3.2 |
| Precision Cruise Missile | 3.5 |
| Cruise Missile | 4.5 |
| Auto-Targeting Cruise Missile | 4.5 |
| Rage Rocket | 4.5 |
| Citadel Cruise Missile | 4.5 |
| Fury Heavy Missile | 4.5 |
| Heavy Assault Missile | 4.5 |
| Javelin Heavy Assault Missile | 4.6 |
| Fury Cruise Missile | 4.7 |
| Rage Heavy Assault Missile | 4.8 |
| Torpedo | 5 |
| Javelin Torpedo | 5.2 |
| Rage Torpedo | 5.2 |
| Citadel Torpedo | 5.5 |
Analysis of the Equation
As of as of EVE release 118.6, the term (ln(drf)/ln(5.5) has been pre-calculated and is stored in the variable: aoeDamageReductionFactor (ADRF). Thus, the equation can be written in this format:
damage created = base damage * min[1, S/E, (S/E*Ve/Vt)^ADRF]
This means that the base damage is multiplied by the smallest of either 1, S/E or (S/E*Ve/Vt)^ADRF. In the equation, then, the number 1 represents 100% of the base damage – since if either of the other values is bigger than 1, they are rejected. Thus, the damage created can be no higher than 100% of the base damage.
When the target's signature radius is larger than the missile's explosion radius, S/E will be greater than 1, and that term will be rejected. If S is smaller than E, then S/E will be computed and compared with the third term. The smaller of these will be chosen and multiplied times the Base Damage.
Since the part of the equation that is affected by velocity ... (S/E*Ve/Vt)^ADRF ... only matters if it is less than 1, it can be set to 1 and solved to find the point where it begins to matter. Doing that gives Vt = S/ (1^(1/ ADRF) * E) * Ve. Since 1^x = 1, then 1^(1/ ADRF) also must equal 1, and the equation reduces to Vt = (S/E) * Ve. This can be rewritten as
Vt = S * Ve/E
Since Ve and E are both attributes of the missile, Ve/E can be combined into a single "minimum velocity factor" for each missile class.
| Missile | Minimum Velocity Factor (Ve/E) |
|---|---|
| Citadel Torpedo | 0.0100 |
| Citadel Cruise Missile | 0.0166 |
| Rage Torpedo | 0.0938 |
| Fury Cruise Missile | 0.105 |
| Javelin Torpedo | 0.158 |
| Torpedo | 0.158 |
| Auto-Targeting Cruise Missile I | 0.230 |
| Cruise Missile | 0.230 |
| Precision Cruise Missile | 0.263 |
| Fury Heavy Missile | 0.451 |
| Rage Heavy Assault Missile | 0.517 |
| Auto-Targeting Heavy Missile I | 0.648 |
| Heavy Missile | 0.648 |
| Precision Heavy Missile | 0.777 |
| Heavy Assault Missile | 0.808 |
| Javelin Heavy Assault Missile | 0.808 |
| Fury Light Missile | 2.05 |
| Auto-Targeting Light Missile I | 3.40 |
| Light Missile | 3.40 |
| Rage Rocket | 4.67 |
| Precision Light Missile | 5.11 |
| Javelin Rocket | 7.50 |
| Rocket | 7.50 |
So, the target velocity at which the damage created begins to be reduced is equal to the signature radius of the target times the minimum velocity factor.
Vt = S * MVF
This means that a rocket will begin doing less damage when the target velocity is at 7.5 * S, a light missile at 3.4 * S, and a torpedo at 0.158 * S. Thus, the same sized ship has to be going much faster to reduce damage from a rocket than it does to reduce damage from a torpedo.
The equations also show that there is a minimum speed that a ship needs to fly before its velocity can reduce the missile damage at all. If the ship is moving below a specific threshold, the explosion velocity and the speed of the ship do not affect the missile damage. In that case, only the signature radius of the target and the explosion radius of the missile can have an effect, and further decreases in the ship's speed will not increase the damage. However, increases the signature radius can, until the damage reaches 100%.
Examples
Note that all examples assume all 0 skills. Higher acceleration control will result in propulsion mods being significantly more effective at mitigating damage.