Difference between revisions of "Tanking"
m (Add Merge to counter Merge at Passive shield tanking) |
m (→Racial Resistances: well that Maller section got removed) |
||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
''see also: [[Natural Resistances#Tech I armor resistances]]'' | ''see also: [[Natural Resistances#Tech I armor resistances]]'' | ||
| − | One major | + | One major consideration when choosing resistance modules is that different races' Tech 1 ships have slightly different base armor resistances. This is explained in the article on [[Natural Resistances]], however for a discussion of tanking, there are four major takeaways: |
*Amarr ships can generally get sufficient resistances off of only MEMs, Damage Control, and RAH | *Amarr ships can generally get sufficient resistances off of only MEMs, Damage Control, and RAH | ||
*Gallente ships generally need to run one Explosive Membrane, Coating, or Hardener | *Gallente ships generally need to run one Explosive Membrane, Coating, or Hardener | ||
Revision as of 06:10, 18 September 2021
Tanking is the art of fitting a ship with modules in order to improve its defensive capabilities to resist, absorb, or mitigate incoming damage, thus preventing or delaying your ship's destruction.
Tanking Basics
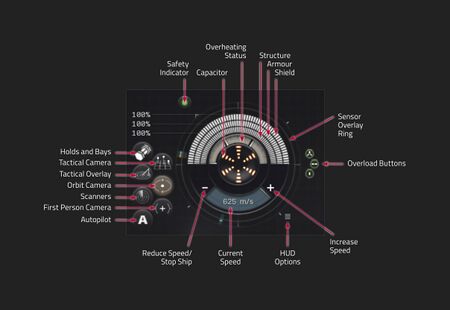
The amount of hitpoints on your ship is represented by the Ship Status Panel - the three rings on the top of the status panel represent, from outermost to the inner ring: your ship's shield, armor and structure (also called "hull"). As you incur damage, each ring will fill with red coloring, starting with your shields, then your armor, and finally, your structure. When the structure ring is completely red, that means your hull has been breached, and your ship is destroyed - and you'll find yourself floating in space in a pod.
To avoid finding yourself floating in your pod you need to be able to tank the damage. This is generally achieved through three ways:
- Increase ship raw HP. Generally known as buffer tanking.
- Repair damage received. Known as active tanking. Passive shield tanking is a special case.
- Increase damage resists. Used to increase effectiveness of both passive and active tanking.
Buffer tanking
The buffer tank is based around the principle of having high damage resistance and as many hit points as possible, thus increasing the Effective HitPoints (EHP) of the ship. The concept behind this is simple, add enough EHP to your ship to outlast your opponent through the use of active and/or passive resistance modules, which complement the HP increasing modules that add raw hit points.
This type of fitting uses a minimal amount of capacitor to run hardeners making it easily sustainable, but can be made fully passive by using only passive resistance modules instead. The primary drawback to Buffer Tanking is that you have no way to repair yourself, so when you run out of hit points you are toast.
Most common in fleet PvP, but also group PvE with logistic support (like incursions, wormhole anomalies / signatures and a few others). In PvP, a fleet will overwhelm an active tank in fairly short order, whereas a buffer tank will give you more survival time. Although, some ships with faction gear and active tank bonuses can field some extremely resistant active tanks that can take on more than you might think.
The effective hitpoints are product of raw HP and resist. In general if you are expecting to have Logistical support (friends to rep your armor) then you want to buffer tank more towards resistance, because the higher your resistances the more effective logistic reps are. While if you don't expect logistical support, you only care about the Effective Hit Points, so whatever combination gives you more effective hit points is the best option.
Active tanking
Active tanking is most commonly used for solo activities such as mission/complex running, ratting, and solo PvP. Active tanking differs from buffer tanking in that it uses armor repair or shield booster modules to actively repair damage done to the ship. You should be careful to include enough resistance and buffer to keep your repair modules from being overwhelmed by incoming damage; frequently this means packing resistance modules (either passive or active) that compensate for the specific types of damage you expect to be receiving.
This type of fitting takes a lot of capacitor to sustain your cap-hungry repair modules so it should ideally include modules such as cap rechargers, capacitor batteries or capcitor rigs to balance out and maintain capacitor stability.
Active Tanking uses energy from the ship's capacitor to run a local repair module. Active tanks are stronger against higher bursts of damage but tend to drain the pilot's capacitor over time resulting in the tank 'breaking' during long engagements and are vulnerable to Capacitor Warfare that drains the ships capacitor dry.
Capacitor stability is important because it allows you to leave your tank modules turned on without ever worrying about running out of capacitor. So long as incoming damage is less than what your repair modules can handle your ship should be able to sustain that level of damage indefinitely. This is commonly referred to as perma-tanking. If incoming damage exceeds your repair capacity you will gradually run out of Hit Points and die. This is commonly referred to as breaking the tank.
For PvP purposes, a cap booster can be used to temporarily supplement capacitor output to allow for short bursts of heavy tanking. The primary drawback to this approach is that unlike the capacitor stable fitting described above, when you run out of charges to run your capacitor booster, you quickly run out of capacitor, your tank will fail and you will die horribly. Cap boosters, will also offer some safety against neuting allowing you to keep on cycling modules even when your capacitor disappears in few seconds.
Similarly, weapon systems that drain your ship's capacitor will effectively disable your active tanking modules. As above, your tank will fail and you will die horribly. In this case, the capacitor booster can be used on an otherwise capacitor stable fitting to provide emergency power to prevent being drained and destroyed.
Ancillary Repair Modules
Ancillary Armor Repairers (AAR) and Ancillary Shield Boosters (ASB) are another way to field strong active tank for a short duration. These modules can be loaded with Nanite Repair Paste (armor) and Cap Boosters (shield). While these modules have charges, ancillary armor repairers repair far more hitpoints than any other repair module, and ancillary shield boosters consume 0 capacitor to cycle. However, once their charges run out (in general after 8 cycles for an armor repairer or 9 cycles for a shield booster), the armor repairer becomes very weak and inefficient, and the shield booster becomes prohibitively capacitor-intensive. Ancillary repair modules have a 60 second reload time to reload their charges. Only one ancillary armor repairer, or capital ancillary shield booster, can be fitted to a ship. Because of the combination of reload time and charge consumption, ancillary repair modules are almost never used in PvE, however they are very popular in solo PvP.
The size of charges used and the rate at which they are consumed is based on the size of the module. Larger ancillary armor repairers hold more paste, but consume more paste per cycle, and larger ancillary shield boosters require larger cap charges to be loaded. While ancillary shield boosters may have multiple different sizes of charges loaded, larger charges offer no benefit over smaller charges (and with their larger volume, allow fewer charges to be loaded at once), and so only the smallest available charge should be used.
Because Overheating repair modules increases both the cycle speed and the amount of hitpoints repaired, ancillary repair modules should always be run overheated to maximize the value of their limited cycles. (The overheat damage sustained can then be repaired while the modules are reloading.)
Resists
Resists on a ship will reduce the damage taken. It is a number that tells you by how large a percentage the incoming damage is reduced. For example 30% thermal resistance on shields means that all incoming thermal damage is reduced by 30%.
The T1 ships have almost identical base resist values but many of the T2 ships have so called "T2 Resists" that drastically vary between races. For example Minmatar ships with T2 resists have massive EM and thermal resists even on shields but have low resists against explosive and kinetic.
But the base resists of a ship are almost always modified by modules fitted on the ship. Resistance percentages are calculated in a way that many people find confusing. A module may list itself as having a 30% bonus to resistances -- but the only time you'll actually see a 30% increase in resistance when using it is if your current resistance is 0%.
The way the calculations work is that the percentage is applied to the remaining damage after resists. If things didn't work this way, you'd easily get resistances above 100%, and shooting you would cause armor to grow on your ship.
Resistances are easier to figure out if you think in damage vulnerability rather than damage resistance. A ship with 60% EM resist is then 40% EM damage received. Adding a 30% resist module multiplies the damage taken by 0.7 so you now take 0.7*0.4 = 0.28 = 28% of the raw damage.
Because of stacking penalties, and the way resistances multiply together, it is not possible to be 100% resistant to a damage type[1]. The final resist with multiple modules and stacking penalties can be calculated with formula
- [math] \text{Resist} = 1 - ( 1 - R_0 )( 1 - R_1)( 1-R_2 \times 0.869)( 1 - R_3 \times 0.571)( 1 - R_4 \times 0.283)...[/math]
where R0 is the hull resist and R1, R2, R3,... are module resists in descending order.
It's often more sensible to increase the resistances of your ship than to increase the total number of raw HP. The damage reduction of resistance modules is a constant where as the buffer reduces with each attack. The fitting requirements for resistance modules are often less than the fitting requirements for Shield Extenders and armor plates. The one drawback is stacking penalties that will inhibit the effectiveness of additional resistance modules but do not apply to Shield Extenders.
Negative resists
Certain effects will apply negative resists to a ship. These include incursion effects, Abyssal Deadspace effects and phenomena generators. The way these are applied may seem confusing but they are simpler than they seem. The idea is exactly same as with normal resists explained above where the percentage change is applied to vulnerability (100% - resist) instead of resist.
A 50% resist penalty means that your ship will take 50% more damage.
Example: You fly your ship with 70% resist into a situation where you receive 50% resist penalty. Your new resist is 55%, how can this make any sense?
Your ship has 70% resistance meaning you will receive 30% of the incoming damage. If 50% resist penalty is applied on your ship you will take 50% more damage. You will be receiving 1.5×30% = 45% damage after your resists. So the new resistance is 100% - 45% = 55%.
The math is simply:
- [math] \text{New resist} = 1 - ( 1 - \text{Original resist} ) \times ( 1 + \text{Penalty} ) [/math]
The resist penalties will never cause the ship to have below 0% resist. If the penalty is big enough that the new resist would be negative the new resist will simply be 0%.
Armor tanking
General Approach
Armor tanking emphasizes the use of Low slot modules to increase armor hit points, resistance to damage, and gain the ability to repair damage taken by armor. Regardless of the approach taken to armor tanking, understand that armor on T1 hulls has an inherent weakness to Explosive damage, and usually a mild weakness to Kinetic damage, and thus you should plan your resistance modules accordingly.
Armor-tanked ships generally have much stronger buffers than shield-tanked ships. This is aided by Armor having near-universally higher base damage resistances than shields (albeit with the opposite order of strengths and weaknesses), and several modules which increase armor hitpoints and resistances which have no shield equivalents.
Armor Repairers are more capacitor-efficient than Shield Boosters (in terms of HP recovered per GJ Capacitor used), and they repair large amounts of HP on every cycle. However, they also cycle very slowly, meaning that they effectively restore less HP per second than shield boosters; and the HP gained is applied at the end of the module cycle (rather than the beginning as it is for shield boosters), meaning that a pilot must anticipate when the repairs will be needed several seconds in advance.
Armor tanking modules generally do not use nearly as much CPU as shield tanking modules. (Some armor tanking modules even consume no CPU at all!) However, Armor Plates and Armor Repairers use much, much more Powergrid than any shield-tanking modules. Furthermore, because armor tanking modules take up Low slots, they leave their ship's Mid slots free for capacitor modules, Electronic Warfare modules, and damage application modules, which gives armor-tanked ships much more utility and versatility than shield-tanked ships. However, in exchange, because armor takes up low slots, and damage-increasing modules also take up low slots, armor-tanked ships generally have lower potential damage output than shield-tanked ships.
Once a ship's armor is depleted, only its hull stands between it and death. This means that, in theory, armor-tanked ships have smaller safety margins than shield-tanked ships. However, this is also fact that Gallente ships are well aware of and, in fact, designed around: Gallente ships commonly feature bonuses to local armor repair modules, and Gallente ships also have the thickest hulls of any ships.
Armor Plates have a unique penalty to them: increased ship mass. This penalty reduces ship agility (acceleration and alignment time), and reduces the speed bonus gained from Propulsion equipment. Armor Rigs also (usually) reduce ship max speeds. As a result, heavily armored ships tend to be significantly slower than heavily shielded ships.
Racial Resistances
see also: Natural Resistances#Tech I armor resistances
One major consideration when choosing resistance modules is that different races' Tech 1 ships have slightly different base armor resistances. This is explained in the article on Natural Resistances, however for a discussion of tanking, there are four major takeaways:
- Amarr ships can generally get sufficient resistances off of only MEMs, Damage Control, and RAH
- Gallente ships generally need to run one Explosive Membrane, Coating, or Hardener
- Caldari ships are generally not armor-tanked at all, however on the rare occasion that they are, they generally need an Explosive, and possibly a Kinetic, resist module
- Minmatar ships generally need to run both an Explosive and a Kinetic resist module, or in extreme cases run full "Rainbow -1"
The reason for these takeaways is that one of the general goals in resistance modules is to have all four of your ship's resistances be at some fairly equal high value; and because different races have different base values, different amounts of effort are required to even the numbers.
Rainbow -1
"Rainbow" tanking refers to an attempt to maximize damage resistance by running one pure resistance module for each of the four damage types. This is generally only done on Battleships or Capital Ships, because of the large number of slots require to do it. However, because of how base resistances, rainbow tanking is generally not quite the most efficient way to maximize resistances. What is generally more efficient is "Rainbow -1": One Membrane or Hardener for each of Explosive, Kinetic, and Thermal, and then a single Multispectrum Energized Membrane. This strategy takes advantage of armor's naturally high EM resistance, improves the other three resistances to match, then uses a single Multispec to further improve everything. This has the added advantage of only applying 1 layer of Stacking Penalties to most resists and no Stacking Penalties at all to the EM resist, and synergizes very well in a fleet setting with Armored Command Bursts.
Armor tanking modules
| Armor plates increase the ships armor HP by a flat number. The drawback is increased mass that results in slower and less agile ship. It is somewhat common to fit oversized plates. For example 1600mm plates on a cruiser. | |
| Energized membranes are passive modules which increase armor resists. The resist bonus is increased by Armor Compensation skills.
Energized Membranes come in 5 types: one for each type of damage, and one Multispectrum which moderately resists all damage. | |
| Resistance coatings are passive modules which increase armor resists. The resist bonus is increased by Armor Compensation skills. Resistance Coatings give smaller bonuses than Energized Membranes, and are generally much cheaper to buy, however they do not cost CPU to fit and so are very useful on ships with limited fitting space.
Resistance Coatings come in 5 types: one for each type of damage, and one Multispectrum which moderately resists all damage. | |
| Armor hardeners are active modules which significantly increase one of the four armor resistances. They consume small amounts of Capacitor energy to run, and slightly more CPU to fit than Energized Membranes. They can also be Overheated for a further increase in strength, however they do not benefit from Armor Compensation skills.
(Active) Armor Hardeners come in 4 types: one for each type of damage. | |
| Damage control is a passive module that increases a ship's shield, armor, and hull resists. This module is not stacking penalized with most other resist modules. Only the Reactive Armor Hardener is stacking penalized with damage control. | |
| Reactive armor hardener is a active module that increases armor resists. it gives in total 60% resist bonus split across all four damage types. When you first activate the module the resists are evenly split to 15% per damage type. As you receive armor damage, the RAH will adjust its resist at the end of each cycle by increasing the resist against the highest received damage types, and reducing the resist against the other damage types. The resists shift by 6% per cycle per resist which is changing. This module is not stacking penalized with other modules except for Damage Control. | |
| Armor repairers are modules that consume moderate amount of capacitor and use that to repair the ship's armor. The capacitor is consumed at the beginning of the cycle but the repair happens at the end of the cycle. | |
| Ancillary armor repairers ("Ancils") are similar to normal armor repairers. These modules can be loaded with Nanite Repair Paste to drastically increase the repair amount for the first 8 cycles it is used. With paste the ancillary armor repairers repair considerably (~1.7x) more than normal T2 armor repairers. Each cycle consumes nanite paste (1 for small, 4 for medium, 8 for large). Once the paste runs out the module can still be used, however without paste the ancillary armor repairers repair considerably (~0.6x) less than T2 normal armor repairers. Reloading the paste takes one minute. During this time the module can not be used. As such, it is commonly recommended that pilots Disable Auto-Reload for ancillary armor repair modules, so that the module does not spontaneously become unavailable at an inopportune moment.
Ancillary Armor Repairers are almost exclusively used in PvP to provide strong burst of active tanking. Usage in PvE is generally not recommended due to the added cost of nanite paste the unsustainability of the repair strength. (However this said, Ancils are still popular in Abyssal Deadspace.) Because of the limited number of full-strength cycles the module can perform, Ancillary Armor Repairers should always be run Overheated; and because of their extremely powerful repair cycles, Ancils are often only activated for single cycles at a time. | |
| Layered Energized Membranes are passive modules that increase ship's armor by a percentage amount. These are very rarely used, as a plate and resist module are usually better than this module. | |
| Layered Coatings are passive modules that increase ship's armor by a percentage amount. These are less effective than the energized membrane variant but do not cost CPU to fit. These are almost never used, as plates and resistance modules are more effective in almost all cases. | |
| Remote armor repair systems consume capacitor to remotely repair armor on single target. The repair again happens at the end of the cycle. This can make it hard to repair targets if they die before the repair lands. Fairly short range when not fitted to a dedicated Logistics Frigate or Logistics Cruiser. Relatively long optimal range but short falloff range; as a result the effectiveness drops rapidly if the target is beyond optimal range. | |
| Ancillary remote armor repair systems are the remote counterpart of local ancillary armor repairers. Like the local ancillary armor repairers These can be loaded with nanite repair paste for 8 cycles of increased repairs. However, once the paste runs out they will repair less than normal remote repairers. | |
Rigs
Tech II Armor Rigs tend to all be very expensive because of the rarity of one component (Intact Armor Plates) which they all use. | |
Implants
| |
| Exile medical booster greatly increases the ship's active armor repair amount, however they carry a chance to reduce your Armor hitpoints, capacitor capacity, turret tracking, or missile damage application. |
Armor Tanking Skills
- Hull Upgrades
- 5% armor HP per level
- Required for armor plates, hardeners, membranes, and resist plates.
- Mechanics
- 5% hull HP per level
- Required for armor repairers
- Repair Systems
- 5% reduction in armor repair module cycle duration. It should be noted that a reduction in activation time increases the capacitor need of the module.
- Required for armor repairers
- EM Armor Compensation, Thermal Armor Compensation, Kinetic Armor Compensation, Explosive Armor Compensation
- 5% increase per level in the corresponding resist for membranes and resist plates
- Armor Rigging
- Reduces the drawbacks of armor rigs by 10% per level.
- Armor Layering
- 5% redution in mass penalty of armor plates per level.
- Resistance Phasing
- 10% reduction in cycle time and 15% reduction in capacitor usage of Reactive Armor Hardener (and Capital Flex Armor Hardener) per level.
Shield tanking
Shield Tanking: Focuses on maximizing your shields' ability to withstand and/or repair damage. This is the most common type of defense for ships with larger numbers of mid-slots, where most shield modules are fitted. It should be remembered that shields on T1 hulls are naturally weak to EM damage.
The versatility of shield modules is somewhat more limited than that of armor modules. Most notable is the lack of good passive shield hardeners. As a result even buffer fit shield ships are often vulnurable to suficiently large number of neuting.
Shield modules generally fit on mid slots. This leaves low slots for damage modules, fitting modules or piloting modules. As a result shield ships generally have higher damage output than their armored cousins. But on the other hand using mid slots for tank limits the ship fit into more or less pure damage dealing as the tank competes with tackling, EWAR, and propulsion modules.
Shield extenders and shield rigs have penalty to the ship's signature radius. This makes it easier to hit shield ships. Shields generally also have less buffer than armor ships. This is most notable when fighting against ships larger than your own.
Unlike Armor Repairers, Shield Boosters give the boost at the beginning of the cycle time instead of at the end, meaning you can wait until you need the shields to activate the shield booster instead of activating it in anticipation of needing it, as is commonly done with armor repairers. Shield boosters also repair much faster and more than armor repairers. This comes at cost of using more capacitor.
After shields are exhausted there is still some armor and hull remaining, leaving a little more room for error.
Shields heal themselves over time at a natural recharge rate. Armor and Hull damage taken is going to sit there until it is repaired. This passive regeneration is taken to extreme on passive shield fits described below.
In short the advantages of shields are:
- Does not reduce speed or maneuverability.
- As a first line of defense, leaves you with Armor and Hull as a fallback if shields go down.
- Recharge on their own – no need to dock for repairs.
- Shield boosting modules work more quickly than armor repair modules and apply effects immediately.
- Low slots are available for weapon enhancing modules.
And the disadvantages of shields are:
- Increases signature radius – ship becomes easier to hit.
- Fewer kinds of enhancement modules – less choice than with armor.
- Shield recharge modules use more capacitor than armor repair modules.
- Mid slots are not available for EWAR, tackle or propulsion modules.
Passive Shield Tanking
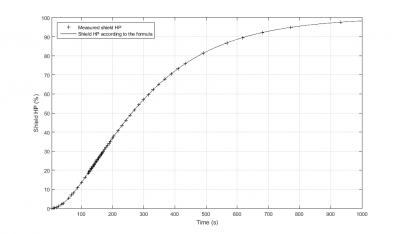
Unlike Armor hit points, shields will recharge themselves after taking damage. The Passive Shield tank is designed to maximize this natural recharge rate without the use of active Shield Booster modules. The shields of a ship have two stats that are relevant to passive recharge: Shield capacity and shield recharge time. The shield capacity is simply the maximum HP for the shields while the recharge time tells how long it takes for the shields to recharge.
The concept behind the Passive Shield Tank is deceptively simple: find a ship with a relatively high natural recharge rate (Shield HP / Recharge time = Average recharge rate), then add as many additional shield hit points to your ship as possible using shield extenders. Because the recharge time for a given ship is a fixed amount no matter how many points of shields you have, adding multiple shield extenders not only adds a lot of buffer, it indirectly increases the recharge rate because more Hit Points are being recharged in the same amount of time. Now add passive modules that increase the recharge rate even further, such as Shield Rechargers, Shield Power Relays and Power Diagnostic Systems; and you have a monster sized Buffer tank that regenerates very quickly without using any capacitor making your defense invulnerable to weapons that drain the capacitor. Shield Flux Coils also increase recharge rate, but should be avoided because they also lower your shield hit points, which is self defeating for the same reason adding Shield Extenders improves your recharge rate.
As the name implies, a fully passive tank does not require any modules that need to be “turned on” to function, and therefore does not require capacitor. The drawback to Passive Shield tanking is the number of modules required to pull it off, which leaves very little room to fit other useful modules such as damage improvement and tackling equipment, which makes this fitting of limited use outside of mission running and bait ships.
While this fitting is more about raw hit points than it is damage resistance adding resit modules will greatly increase the effectiveness of passive recharge. Shield resistance amplifiers can be added to provide a little damage reduction. Some people use Multispectrum Shield Hardeners and Shield Hardeners to improve damage resistance, but these are active modules that require capacitor, thus making your Passive Shield tank not quite passive any more. This can be problematic because the Shield Power Relays you depend on to increase your shield recharge rate also totally gimp your capacitor recharge rate. For this reason careful balancing is necessary to make the Passive Shield Tank effective. When done correctly, however, Passive Shield tanking can be used to handle tough missions with a single ship.
It is generally advised NOT to mix modules that increase shield recharge rate with modules that repair shield damage.
Active Shield Tanking
Active Shield Tanking is most commonly used in higher-level PvE, but also has a place in solo or small-gang PvP. Active Shield Tanking is based on using a Shield Booster to recover your shield HP faster than an enemy fleet's damage can deplete it. The high Capacitor costs of Shield Boosters mean that active shield tanking is most commonly done on Battleships or Tech 2 and Tech 3 Cruisers, as their larger CPUs, Powergrids, and Capacitors give more room to achieve stability, while their T2 Resists amplify the effectiveness of their shield boosters. Active shield tanking is generally not preferred in larger-group activities, as an active shield tank can be easily overwhelmed if the pilot is outnumbered too heavily.
Understand Shield Recharge Rate
It is valuable to understand the mechanics of shield recharge rate. All ships have shields, and all shields have a recharge rate. Therefore, this concept applies to every ship, shuttle, and pod in Eve, and thus to every pilot who undocks.
NOTE: The math behind the shield recharge rate calculation is the same as that used for a ship's capacitor recharge rate.
In a ship's information screen, on the attributes tab, under the shield heading, is listed the total shield amount of the hull, and the shield recharge time. The recharge time expresses how long it will take to go from 0% shields to roughly 98% shields when the ship is sitting idle in space and no one is repairing the shields or damaging them. That last ~2% of your shields will take much longer.
But shields do not recharge at a constant rate. Imagine a ship with a 440 shield and a shield recharge time of 440 seconds. To find out how many shield points you regain per second you might divide: 440 shields / 440 seconds = 1.0 shields per second.
That is close but not quite correct. The average shield recharge rate is going to be 1.0 shields per second but sometimes it will be higher, and sometimes it will be lower.
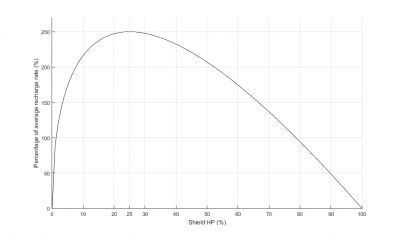
The actual behavior is that when the shield is near 0% or 100% it replenishes slower. The peak recharge rate will be 2.5x the average rate and will occur when the shields are damaged to 25% of shield maximum capacity.
Shield recharge rates above ~98% shield is extremely low. For ships with small shield capacity it is essentially non-existent. The shield recharge rate also drops sharply below 25% capacity. Once shields have been damaged beyond 25% the passive tank "breaks" and the ship dies shortly.
As the shield takes damage, its level goes down. In response, the rate at which it rebuilds itself goes up. The increase in shield recharge rate continues until it peaks at 25% of shield capacity. At this threshold, the default ship Health Alert noise will sound to warn the pilot that the shield is at its recharging limit. If it continues to take more damage than it can hold, the regeneration will drop off quickly. This means if constant damage is applied, the shield will regenerate less as it becomes empty, thus making it easier to shoot the armor below it.
The math for shield regeneration is exactly the same as that of the capacitor recharge rate. Two numerical attributes are required: shield capacity, and shield recharge time. These are both displayed in the ship's "show info" attributes panel in-game, below its capacity. Note that modules that refer to "recharge rate" modify the recharge time number, not the raw regeneration in HP/s.
- [math] \displaystyle\frac{\text{d}C}{\text{d}t} = \frac{ 10C_{\rm{max}}}{T} \left( \sqrt{ \frac{C}{C_{\rm{max}}} } - \frac{C}{C_{\rm{max}}} \right) [/math]
...where:
C is your current shield HP.
Cmax is your maximum shield HP.
dC/dt is your current shield regeneration in HP/s.
T is shield recharge time.
- Consequences
The fact that these attributes are both set has some interesting consequences. Notably for this calculation, recharge time is not dependent on anything else, including maximum shield capacity--as you might have intuitively expected. This has the effect that if two ships have the same "recharge time" attribute, and one has more capacity, then the one with the larger capacity will get more raw HP/s regeneration, and appear to 'repair faster' despite reaching its maximum level in the same time. In simple terms, recharge is calculated by percentage first, which is then translated into HP/s of regeneration. So maximum capacity indirectly affects the amount of HP/sec regenerated, having the effect that Extender modules increase regeneration, and flux coils become much less useful compared to Rechargers or Power Relays.
- Calculating Average rate
The average shield regeneration per second can be computed by dividing the shield capacity by its recharge time.
Average HP/s = Shield maximum / Recharge time
The peak recharge Rate is 250% of average shield recharge. It occurs when the capacity of the shield is at 25% of its maximum value. Shield recharge rate drops rapidly once the shield falls below 25% of shield capacity.
Fitting a shield tank
In many cases the technical construction of the ship dictates the use of Shields (or Armor) as its primary defense. Any ship receiving a bonus to shield capabilites would likely use shields. And because most shield modules use medium power slots, a ship with more mid than low slots will tend to use shields. Though the purpose of the ship can never be ignored. As a shield ships use mainly mid slots for defence they can fit much higher damage output and are often faster.
Every ship has a shield. Whether or not a pilot decides to expand and improve the shield is his or her choice.
That said, here are the factors that you look for when you are thinking about shields:
- Shield specific hull bonus.
- Surplus of mid slots or shortage of low slots.
- More need to favor modules that improve weapons (which tend to need low slots).
- Less need for EWAR modules (which tend to need mid slots).
| Shield extenders increase ships shield HP by a flat number. The drawback is increased signature radius that makes the ship easier to hit. Oversized modules are often used (Medium size on a Frigate class ship, for example). | |
| Shield hardeners are active modules that increase ship's shield resists. Multispectrum Shield Hardener increases resist to all damage types but less than type specific modules. The name is misleading and the module does not adapt to damage like the reactive armor hardener. Active shield hardeners are considerably more effective than the passive shield resistance amplifiers. | |
| Shield resistance amplifiers are passive modules that increase ship's shield resists. Easier to fit than active hardeners and do not need any capacitor. Considerably lower resist bonus compared to active hardeners. The resist bonus increases with appropriate shield compensation skill. There is no resistance amplifier that increases all resist types like there is for armor. | |
| Damage control is a passive module that increases ship's shield, armor and hull resists. This module is not stacking penalized with any other shield resist module. | |
| Shield power relays are passive modules that increase ship's shield recharge rate at the cost of reduced capacitor recharge rate. This module defines a passive shield tank. Since the relay modules fit in low slots, this means more Extenders may be fitted alongside them. On the other hand, this also means no low slot weapon upgrade modules for high damage. This will limit the situations where a passive tank may be used. One of the few low slot shield modules. | |
| Shield flux coils are passive modules that increase ship's shield recharge rate at the cost of reduced shield capacity. The reduced shield capacity reduces the shield recharge rate but the recharge rate bonus on flux coils is larger than on power relays resulting in higher recharge rate. | |
| Shield rechargers are passive mid slot modules which provide a modest increase to the shield recharge rate. If there is fitting room for shield extender then that may be a better choice. | |
| Shield boosters consume ship's capacitor to repair (or boost, as the name says) the shields in exchange. Note that the repair happens at the beginning of the module cycle. Shield boosters generally have short cycle time and mediocre capacitor:hitpoint rate compared to Armor Repairers. | |
| Ancillary shield booster provides a capacitor-free method of active shield tanking for limited time. They can be loaded with Capacitor Booster Charges, and will consume the loaded charges upon activation. When no charges are loaded, it will consume quite a large amount of capacitor instead. They will reload in 1 minute (60 seconds). Capacitor Booster Charges of different sizes can be fitted, however it is recommended to use the Navy variant of the smallest charge available (the accepted charge size is displayed on the Show Info tab). Using larger charges offers no benefits. Ancillary shield boosters are almost exclusively used in PvP situations to provide repairs without consuming the precious capacitor. Usage in PvE is not recommended due to the long reload time, the cost of Capacitor Booster Charges and burst tanking nature. | |
| Shield boost amplifiers are passive mid slot modules that increase shield booster repair amount without increasing the capacitor usage. They are completely passive and use only 1 powergrid, however they require quite a bit of CPU. This makes these impractical for smaller hulls due to the limited med slots and fitting resources. However, Boost Amplifiers double the heat damage from overheating. | |
| Remote shield boosters use capacitor to repair shields of a single target. Moderately short Optimal range and long Falloff range. Note that the repair is delivered at the start of the cycle. | |
| Ancillary remote shield boosters are remote shield boosters that can be loaded with cap boosters. They behave exactly the same with local Ancillary Shield Boosters except they repair other ships instead. Usage without Cap Booster Charges are highly discouraged due to the large Capacitor usage. | |
| Power diagnostics systems are low slot engineering modules. Small percentage increase to shield capacity, capacitor capacity, powergrid output, shield recharge rate and capacitor recharge rate. | |
| Capacitor power relays are not exactly a shield modules, but an engineering module. They are a passive low slot module that increase capacitor recharge rate at the expense of reduced shield booster repair amount. These are generally avoided on active shield tanked ships. The penalty does not apply to remote shield boosters. | |
Rigs
| |
Implants
| |
| Blue Pill medical booster greatly increases the ship's active shield boosting amount, however they have a chance to penalize your ship's Capacitor and Shield capacity, your turret's optimal range, or your missile's explosion velocity. |
Shield skills
The following skills are required to field a full Tech 2 Shield tank:
- Shield Management
- 5% increase in shield capacity per level.
- Required for shield boost amplifiers.
- Energy Grid Upgrades
- 5% PG per level. Required for shield power relays and power diagnostic units.
- Shield Upgrades
- 5% reduction in shield extener PG usage.
- Required for resistance amplifier, shield recharger modules.
- Shield Operation
- 5% reduction in shield recharge time per level.
- Required for shield boosters and maximize shield recharge.
- Tactical Shield Manipulation
- Reduces damage bleeding to armor through shields-.
- Required for shield hardeners. No good reason for training beyond IV unless you want to use certain capital modules.
- EM Shield Compensation, Thermal Shield Compensation, Kinetic Shield Compensation, Explosive Shield Compensation
- Increases the specific resist of the passive shield resistance amplifiers.
- Training the four damage type-specific shield compensation skills is less important. The passive Shield Amplifier modules benefit most from them, but are not widely used, but active resistance modules (like Multispectrum Shield Hardeners) get no benefit at all.
- Shield Compensation
- 2% reduced capacitor usage for shield boosters.
- Shield Emission Systems
- 5% reduced capacitor usage for remote shield boosters.
- Shield Rigging
- Reduces the drawbacks of shield rigs.
- Hull Upgrades
- 5% hull HP per level. Required for damage control.
Hull tanking
Hull Tanking is a rare and dangerous art employed only by the pilots with either the most bravery or the thickest of skulls. With hull tanking there is no safety buffer. Once your hull tank is gone your ship goes out in glorious explosion. Additionally, incoming hull damage slowly bleeds into the ship's modules, causing them to artificially burn out and making it unwise to hull tank for long period of time. Hull tanking is also very much an 'all or nothing' affair: it is nearly impossible to repair hull damage without docking in a starbase.
Regardless of these disadvantages, hull tanking is sometimes done unironically, as with certain ships their base hull HPs are so high that a hull tank is actually the best way to maximize their HP buffer. A bait ship with hull tank can lull attackers into a false sense of victory as they see the shields and armor vanish, only to spend ages grinding down the hull. Gallente ships like Hecate, Brutix, and Megathron have notably thick hulls (and very high damage Blaster turrets), making them viable at hull tanking.
As all the practically useful hull tanking modules are passive, a hull tank is resistant to neuting and other forms of capacitor warfare.
| Reinforced bulkheads give a percentage bonus to hull HP. These are the only modules that increase hull HP. | |
| Damage control increases ship's hull resist to all damage. | |
| Hull repairers use capacitor to repair hull. These modules are extremely slow and can not be practically used in combat. | |
| Remote hull repairers allow you to remotely repair another ship's hull. These modules are extremely slow and can not be practically used in combat. No ship is bonused for using these modules. | |
| Transverse bulkheads give a large percentage bonus to hull HP. No other rig gives any bonuses to hull. | |

|
Hull Repair Bots allow a logistics ship to remotely repair another ship's hull. These are the only form of hull logistics that are commonly used, as they count as Logistics Drones and thus receive bonuses from certain Logistics Cruisers. They are commonly used as an emergency backup, to patch up the hull of an allied ship which recently took a little too much heat. |
Hull tanking is improved by only a single skill:
- Hull Upgrades
- 5% hull HP per level. Required for damage control.
Remote repairing
- Main article: Logistics
Remote repairing means that the main fleet outsources the repair duty to dedicated logistic wing. This allows the main fleet to fit large buffer tank that makes them able to survive the alpha of enemy fleet. This also allows the logi wing to focus the repping power of whole fleet on single ship.
Spider Tanking
While normal logistic fleet configuration outsources repairing to logistic wing spider tanking shares the repairing and combat duty between the whole fleet.
In simple terms, Spider tanking involves the use of a Buffer and/or highly resistant tank that is repaired remotely by other ships in your squad who are in turn repaired by remote repair modules on your ship. This is an advanced technique that requires a good deal of coordination to function effectively.
Burst resistance modules
There are also a couple of modules that can be activated to give a short burst of high resistances. Assault Frigates and Heavy Assault Cruisers can equip an Assault Damage Control (or ADC), which gives lower passive resists compared to a regular Damage Control, but can be activated to give a burst of 95% omni resistance to shield, armor, and hull for up to 14.4 seconds with a 150 second reactivation delay. Capital Ships can equip a Capital Hull Emergency Energizer (or CEHE), which only gives a 95% omni resistance bonus to structure, has no passive benefit, and burns out after a single use. Both modules take the place of a regular Damage Control.
References
- ^ It is possible to have over 100% resist by overheating a deadspace hardener on a Deep Space Transport in a red giant wormhole system. This will result in immediate destruction of the ship if any damage is taken so don't do it.